How Do Smartphone Batteries Overheat and Explode and How to Prevent It?
As we’ve reported just a few days ago, the United States Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has now officially confirmed the recall of the Samsung Galaxy Note7. Their decision is a reaction to a total of 35 reported cases of the battery exploding. Among them, a teacher from Essex, UK, who saw her device explode as it was laying on a table while charging.
We’ll cover the following topics here…
- Why Smartphone Batteries Explode
- How Does This Happen in Practice
- How to Prevent Smartphone Batteries from Exploding
- How Do I Know That My Galaxy Note7 Won’t Explode
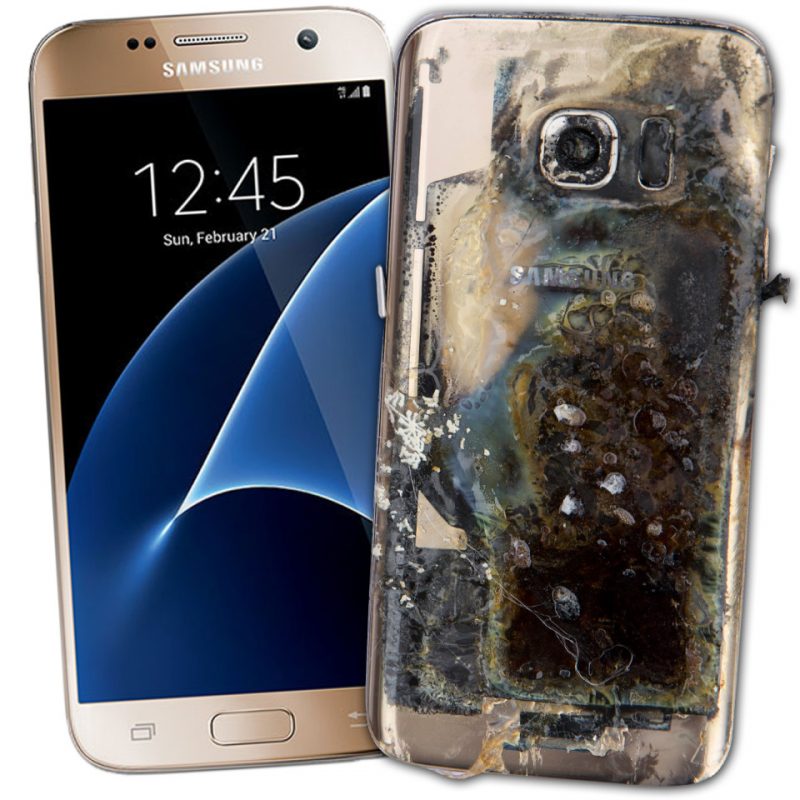

In their official press statement, Samsung said, “We are currently conducting a thorough inspection with our suppliers to identify possible affected batteries in the market. However, because our customers’ safety is an absolute priority at Samsung, we have stopped sales of the Galaxy Note7.”
“For customers who already have Galaxy Note 7 devices, we will voluntarily replace their current device with a new one over the coming weeks,” the company added. Given that Samsung is recalling more than 2 million of Note7 smartphones, things are not looking too bright for their shareholders.
But what about the average Joe with a smartphone in his pocket? Should he be worried? And what exactly caused those 35 Galaxy Note7 smartphones to explode?
Why Smartphone Batteries Explode
Smartphone batteries are not the only type of battery with explosive tendencies. As reported by Futurism, a test drive of Tesla’s Model S ended with the car bursting into flames and the four people who were in the vehicle closely escaping as the Model S quickly turned from a hyper-modern electric vehicle of the future into a smoldering pile of dust.
This was not the first time for the Model S to catch on fire. “Previous Model S fires have been attributed to a puncture in the chassis and the battery back,” explains Jamie Lendino from ExtremeTech. To fix the issue, Elon Musk, CEO and product architect of Tesla Motors, has announced that “all cars produced after March 6 will have three new underbody shields, made of aluminum and titanium.”
As of June 2016, cumulative global sales totaled over 129,000 units, which pales in comparison with the number of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in cordless applications. According to The European Association for Advanced Rechargeable Batteries, above one billion lithium-ion batteries are made every year, and this number is only expected to grow as more people switch to electric vehicles.
What makes lithium-ion battery fires so dangerous, as all firefighters who were called in to put down the blazing Tesla S vehicles found out, is the fact that as water reacts with the lithium, the fire actually gets worse. The firefighters had to seal off the area and spray the car with a special foam used in this type of a situation.
The reason why lithium-ion batteries can explode and burn so violently has everything to do with their design and natural properties. “Lithium is stored in the anode (negative electrode) and transported during the discharge to the cathode (positive electrode) via an organic electrolyte,” explains the Safety of lithium-ion batteries publication from the European Association for Advanced Rechargeable Batteries.
When lithium-ion batteries are in an environment where any excessive heat can be gradually evacuated, the batteries stabilize and progressively cool down. But when the heat cannot be evacuated, which often happens inside a smartphone or a large battery pack of an electric vehicle, the battery temperature will increase, eventually reaching a status where a situation called thermal runaway can occur.
In such situation, an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to devastating results. Lithium-ion batteries are especially prone to thermal runaway because they contain several components which can, under specific conditions, react and generate heat or flames, including the passivation layer, PE separators, PP separators, solvents, binder, and electrolyte.
How Does This Happen in Practice?
“A common source of battery explosion is a user putting a battery in their pocket along with spare change, paper-clips, or other metal objects,” states an article posted on Battery University, a site devoted to the basics about batteries. Even though modern smartphone batteries have very small contact terminals, it’s possible to create a short-circuit, which could lead to a violent explosion.
However, the users who saw their Note 7 devices ignite in flames had the battery inside the smartphone. So, what had happened? According to latest reports, a production error pushed the electrodes inside the battery too close together, leaving little to no room available to keep the positive and negative plates in the battery. “If anything gets in between these two plates, it can cause problems, especially if things haven’t been designed up to the necessary standards, and you then place the battery under the stress of overcharging,” states the Safety of lithium-ion batteries report. In other words, the extra current that occurs during charging caused an internal short-circuit which, in turn, caused the batteries to explode.
As we’ve explained above, when lithium-ion batteries past a certain point, a thermal runaway occurs, bypassing all internal protection mechanics. The explosive Note7 devices had several of them inside, one in the charger, one near the USB port, and another inside the battery itself, but they were all unable to stop the chemical reaction from intensifying.
How to Prevent Smartphone Batteries from Exploding
Samsung has prevented further battery explosions by releasing “a “quick fix” for stubborn Galaxy Note 7 owners who don’t want to return their devices, despite the global recall over batteries that might potentially explode,” states Engadget. This fix limits the Note 7’s battery to 60 percent, hopefully preventing any future overheating issues.
But you don’t have to have the manpower of a large, multinational giant to keep your smartphone battery from exploding. These are out top 5 best tips:
- Only use the manufacturer’s original battery and charger.
- Buy all your accessories from reputable suppliers and manufacturers.
- Never leave your device in hot areas or extreme cold.
- Keep liquids and moisture away.
- Read the instructions for your device and accessories.
For more useful tips on how to prevent your smartphone battery from exploding, read our full article on the topic.
How Do I Know That My Galaxy Note7 Won’t Explode?
In their latest press release, Samsung states, “Our highest priority is the safety of our customers, and we strongly urge Galaxy Note7 users to immediately participate in the replacement program based on local availability.”
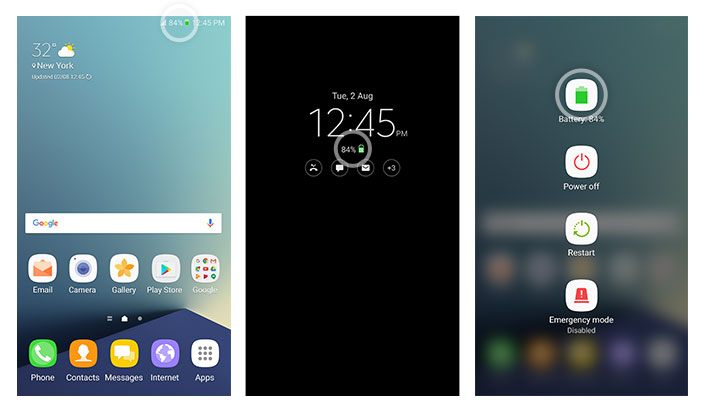
To help their users identify whether their device is affected by the manufacturing flaw, the company has introduced a green battery icon that’s visible on the Status Bar, the Always On Display screen, and the Power Off prompt screen. All devices with the green battery icon are completely safe to use. What’s more, devices from the new batch of Galaxy Note7 smartphones have a square symbol on the label of the packaging box, to help users identify the status of the smartphone even before they take it out the store.